Today, Chartio is announcing Data Stores, a better way to store and transform data. We’ve always been at the forefront of agile business intelligence, and Data Stores makes Chartio even more agile.
Traditional BI tools require costly and time-consuming ETL (Extract, Transform, and Load) and data warehousing processes. This turns BI implementations into elaborate waterfall processes demanding months of requirements planning, dedicated hardware, additional software, and costly consulting - all before you create your first chart.
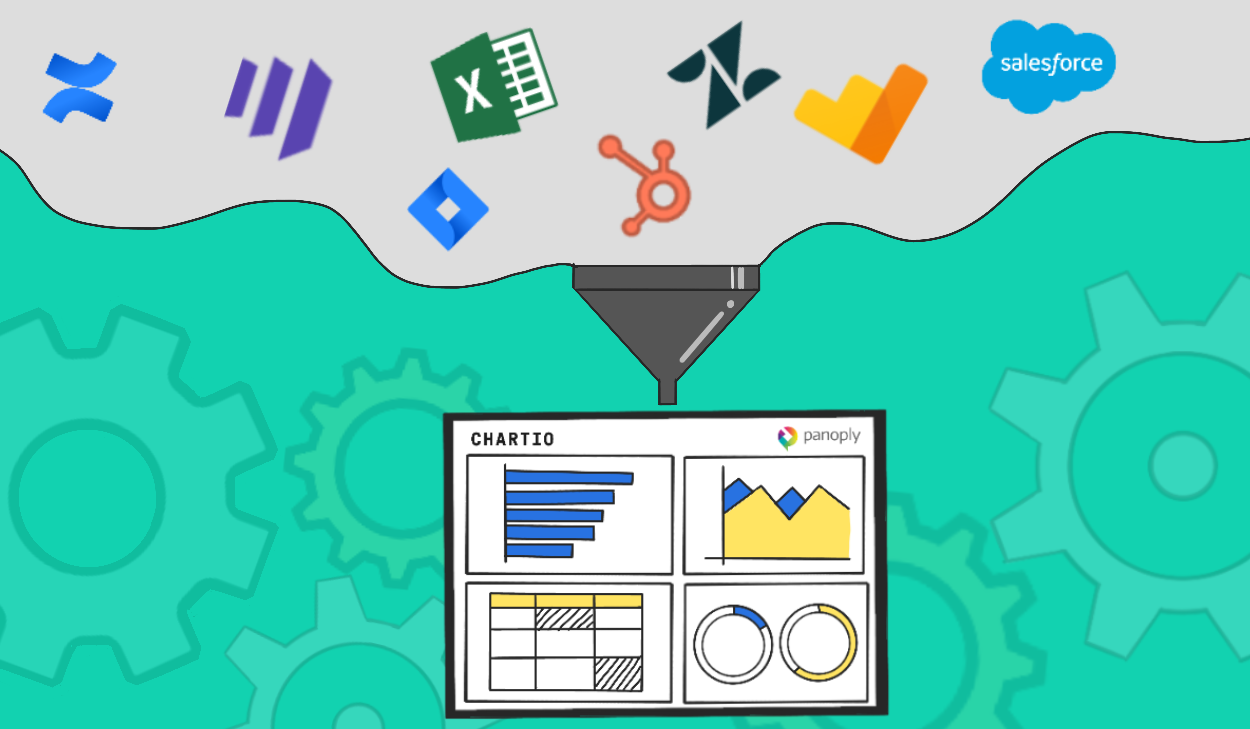
Chartio has always made it possible to skip ETL and data warehousing, with its extensive modeling layer and direct connections to live data. Now, Data Stores simplify ETL itself, using Chartio’s Data Pipeline UI to rapidly layer in summary or rollup tables as needs evolve.
Data Stores allow organizations to change the structure of their data inside Chartio without changes to their operational data. Data Stores eliminate the data warehouse in many situations, by greatly reducing the amount of storage needed and the processing time required to transform data.
Chartio’s vision of making business intelligence as universal as the common spreadsheet requires that business users have access to information. And by simplifying storage, security, and usability, Data Stores give more business users access to better information.
Streamlining Storage
We’ve already explained how to avoid letting data warehousing decisions delay or derail your business intelligence project. In many cases, it’s possible to avoid implementing a data warehouse by storing summary tables. Data Stores streamline that process by enabling you to create your queries in our drag-and-drop interface and store the results in our cloud.
With Data Stores, you can create stored tables the way you’d create any other query in Chartio. You can combine columns from multiple data sources and transform the data using our data pipeline.
Data Stores work just like any other data source on Chartio. Data Stores allow you to take the load off your operational servers by performing summary operations in off-peak hours, and storing the summary information on the cloud, where your queries will not affect performance of the source database.
In the following example, we created a summary table of the number of users and documents created by each customer of our demo digital signature company. This table can now be used in other charts.
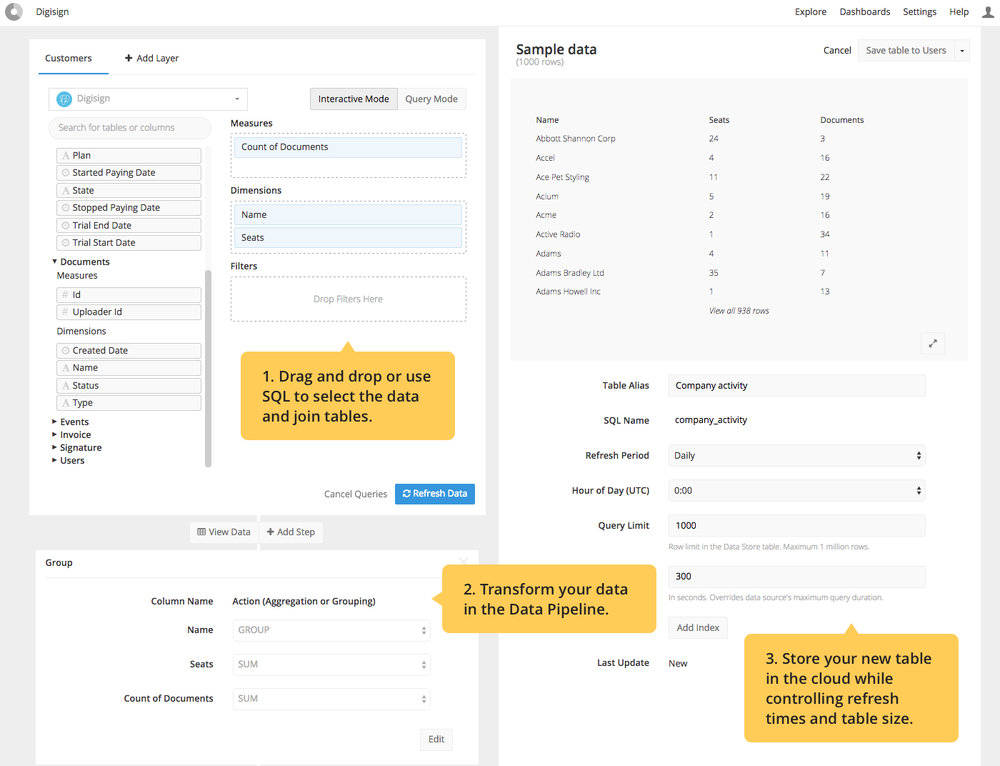
Creating a table in Data Stores uses the same interface as building a chart in Chartio. A Data Store can contain up to one million rows of data.
Improving Usability
Data Stores make business intelligence more usable and accessible.
Business users seldom want or need access to all their company’s operational data. With Data Stores, they only have access to the tables and columns they need. This will not only make it easier for them to build queries, but avoid the problem of overwhelming them with dozens of columns with similar names, and having them query the wrong columns.
To users, Data Stores tables look like any other table in Chartio - only simpler and smaller.
As you learn more about your data and how it’s used, you can use Data Stores to share commonly-used queries and tables of results. This saves business users having to reinvent the wheel, but also helps ensure that everyone is using the same definitions in their data. And it provides the additional benefit of reducing the number of times that these popular and potentially intensive queries are run.
Not all teams in an organization need the same data, and Data Stores give organizations the ability to create sources for the needs of specific teams and to limit access to those sources.
Simplifying Data Access
Data Stores simplify access by giving users only the information they need to do their jobs.
Chartio already gives administrators the ability to limit access to particular sources. Data Stores give even more granular control of what data is seen by whom.
With Data Stores, administrators can create new data sources that eliminate personally identifiable information, or roll up data to remove sensitive information. This makes it possible to limit which columns or rows of a table a user can see. Data Stores make it simple, for example, to keep the Eastern and Western regions from seeing each others’ data; for an analyst to report on individual customers by number, but not by name; or for an assistant to create a report by salesperson without seeing individual transactions.
Enabling Agile Business Intelligence
Data Stores make Agile Business Intelligence possible. Chartio’s customers can implement business intelligence without months of planning and improve their systems continuously - while lowering the risk of unanticipated expenses.
This is an important advance in how business intelligence is deployed. Traditional waterfall processes can involve months of requirements-gathering and design - not to mention implementation - by IT. Agile business intelligence gives users who know they need business intelligence the ability to rapidly implement systems, explore their data, and continuously improve their systems as their needs change.
Data Stores enable agile BI by streamlining storage, lowering the risk to operational systems, giving administrators more control of who can use what information, and standardizing on a common view of what data to use.
Data Stores streamline storage, making it easier than ever to implement a business intelligence system without first buying a data warehouse.
Data Stores improve control of information, making it easier to control the rollout of information in the organization. Over time, Data Stores make it possible to improve the quality of information for all users. The elegant design of the Data Stores model means that organizations can make these improvements without additional consulting and services.